Google AI Essentials
- Introduction to AI
- Maximize productivity with AI Tools
- Discover the art of Prompt Engineering
- Use AI Responsibly
- Stay Ahead of the AI curve.
Introduction to AI
Intelligence: is the human ability to perform congnitive tasks.
Cognitive Task: is any mental activity such as thinking, understanding, learning, and remembering. Cognitive Abilities help humans in making decisions and solving problems. However, there is a limit to how much processing we can do at a time; AI helps extend our cognitive abilities. AI helps us to make better decisions and to solve problems faster.
Artificial Intelligence: computer programs that can complete cognitive tasks typically associated with human intelligence.
AI asists us with tasks using Math to learn from Data.
AI Development Techniques
There are mainly two techniques used to design AI programs:
- Rules-based techniques: involve creating AI programs that strictly follow predefined rules to make decisions. For example, a spam filter using rule-based techniques might block emails that contain specific keywords using its predefined logic.
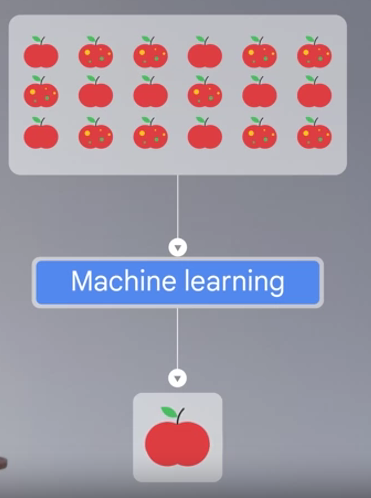
- Machine-learning techniques: involve creating AI programs that can analyze and learn from patterns in data to make independent decisions. For example, a spam filter using these techniques might flag potential spam for the recipient to review, preventing automatic blocking. If the recipient marks emails from trusted sources as safe, the spam filter learns and adapts its logic to include similar emails from that sender in the future.
How does AI use machine learning?
- Recommendation systems (Youtube recommended videos for you) use AI.
- AI Tool is an AI Powered software that can automate or assist users with a variety of user tasks.
- AI systems examples - translations in real time, map software that suggest quick routes.
- AI systems are powered by ML / Machine Learning
Training Set
- ML are as good or as worse as the quality and relevance of their training data.
- A fundamental problem could be a bias within the training data. This can cause AI tool to produce inaccurate or biased / unintended outputs.
Approaches to training ML Programs [ML is a subset of AI]
- Supervised learning:
- Unsupervised learning:
- Reinforcement learning:
Foundations of Generative AI
Capabilities and Limitations of AI
1. Healthcare
Disease Diagnosis and Treatment: AI can analyze medical data to assist in diagnosing diseases and recommending treatments. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns in medical imaging, genetic data, and patient records to identify conditions early.
Personalized Medicine: AI can help tailor treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors, improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
Drug Discovery: AI can accelerate the discovery and development of new drugs by analyzing vast datasets to identify potential compounds and predict their effectiveness and safety.
2. Education
Personalized Learning: AI can adapt educational content to meet the needs of individual students, providing customized lessons, feedback, and assessments.
Automated Grading: AI can help teachers by automating the grading process, allowing them to focus more on student engagement and personalized instruction.
Tutoring and Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual tutors can provide students with additional support and resources outside of the classroom.
3. Environmental Conservation
Climate Modeling: AI can enhance climate models, improving predictions about climate change and helping policymakers make informed decisions.
Wildlife Protection: AI can monitor wildlife populations using drone footage and sensor data, helping to combat poaching and manage conservation efforts.
Energy Efficiency: AI can optimize energy use in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes, reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability.
4. Social Good
Disaster Response: AI can analyze data from social media, sensors, and other sources to provide real-time information during natural disasters, aiding in response and recovery efforts.
Humanitarian Aid: AI can help distribute resources more effectively during crises by predicting needs and optimizing logistics.
Accessibility: AI can develop tools for people with disabilities, such as speech-to-text applications, navigation aids, and personalized assistive technologies.
5. Economic Development
Financial Inclusion: AI can provide financial services to underserved populations, enabling them to access credit, insurance, and other financial products.
Job Creation: While AI may displace certain jobs, it can also create new opportunities in tech development, maintenance, and various support roles.
Agriculture: AI can optimize farming practices by analyzing data on weather, soil, and crops, leading to increased yields and sustainable practices.
6. Governance and Public Services
Smart Cities: AI can enhance urban planning and management, improving traffic flow, reducing pollution, and enhancing public safety.
Fraud Detection: AI can detect and prevent fraudulent activities in public services, ensuring that resources are used effectively and reach those in need.
Policy Making: AI can analyze large datasets to inform evidence-based policy making, helping governments address complex issues more effectively.
7. Research and Innovation
Scientific Discovery: AI can process and analyze large volumes of research data, identifying new patterns and accelerating scientific breakthroughs.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: AI can facilitate collaboration across different fields by identifying commonalities and enabling the sharing of knowledge and resources.
Ethical and Responsible AI
Bias Mitigation: Developing algorithms that are transparent and unbiased is crucial. Efforts to identify and mitigate biases in AI systems will ensure fair and equitable outcomes.
Privacy Protection: Ensuring that AI systems are designed with privacy in mind, using techniques such as differential privacy and federated learning, will protect individual data.
Regulation and Standards: Establishing clear regulations and standards for AI development and deployment will help ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
AI as a collaborative Tool
- Task Management: AI can automate task assignment based on team members' skills and availability, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
- Timeline Prediction: Predict project timelines and identify potential delays by analyzing past project data.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor project progress in real-time, providing updates and alerts for potential bottlenecks.
- Meeting notes, automated.
- Language Translation: Real-time translation services for multilingual teams to facilitate clear communication.
- Speech-to-Text: Convert meetings and discussions into text for easy reference and sharing.
- Chatbots: Provide instant answers to common questions, facilitating smooth internal communication.
- Data Aggregation: Collect and consolidate data from various sources for comprehensive analysis.
- Trend Analysis: Identify trends and patterns in data that can inform strategic decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecast future outcomes and suggest proactive measures based on historical data.
- Document Generation: Automate the creation of reports, proposals, and other documents.
- Real-time Editing: AI-powered tools like Grammarly or Copysmith for real-time editing and content improvement.
- Version Control: Manage document versions and ensure all collaborators are working on the latest version.
- Personalized Learning: Tailor training programs to individual needs and learning styles using AI.
- Knowledge Sharing: AI-driven knowledge bases that provide relevant information and resources to team members.
- Performance Feedback: Continuous and automated feedback on employee performance and areas for improvement.
- Virtual Assistants: AI chatbots to handle customer inquiries, providing quick and accurate responses.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyze customer feedback to understand sentiments and improve service quality.
- Automated Follow-ups: Schedule and send follow-up emails or messages to customers or team members.
- Brainstorming Assistance: AI tools to generate ideas or suggestions based on input criteria.
- Trend Forecasting: Predict market trends and suggest innovative solutions.
- Collaboration Platforms: AI-enhanced platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams to facilitate idea sharing and collaboration.
- Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks and workflows to save time and reduce errors.
- Resource Allocation: Optimize resource use by predicting needs and reallocating as necessary.
- Supply Chain Management: AI-driven insights for better inventory management and logistics coordination.
- Lead Scoring: Identify and prioritize high-potential leads using AI analysis.
- Customer Insights: Gain deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences.
- Campaign Optimization: Automate and optimize marketing campaigns for better reach and engagement.
- Recruitment: Use AI for resume screening, candidate matching, and interview scheduling.
- Employee Engagement: Monitor and improve employee engagement through sentiment analysis and feedback loops.
- Performance Management: Analyze employee performance data to provide personalized development plans.
- Literature Review: Automate the review of scientific literature and patents to keep up with the latest developments.
- Experimentation: Design and analyze experiments using AI to predict outcomes and optimize processes.
- Collaborative Platforms: AI-powered platforms for sharing research data and findings among collaborators.
- Health Monitoring: AI tools to monitor employee health and well-being.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure compliance with safety regulations through automated checks and alerts.
- Incident Prediction: Predict potential safety incidents and suggest preventive measures.
Maximize Productivity using AI Tools
- Brainstorm ideas.
- Text generation for websites.
- Support research on topics.
- Translate content into multiple languages
- Generate images - logo, branding, design visuals, etc.
- Create audio, video for promotional purpposes.
Ways to use AI
- Use as standalone AIs
- Speeko: public speaking AI tutor
- Integrated AI - Adobe Photoshop neurofilter - integrated AI into an existing desktop solution.
- AI Tool chain
- Or a custom solution
AI Models and the Training Process
- Define the problem to be solved. AI designers and engineers want to predict rain to help people stay dry when commuting to and from work. They start by considering AI’s capabilities and limitations before identifying an AI solution.
- Collect relevant data to train the model. AI designers and engineers gather historical data of days when it rained and days when it didn't rain over the past 50 years.
- Prepare the data for training. AI designers and engineers prepare the data by labeling important features, such as outdoor temperature, humidity, and air pressure, and then noting whether it rained. It's also common to separate the data into two distinct sets: a training set and a validati
- Train the model. AI designers and engineers apply machine learning (ML) programs to their rain prediction model, which helps it recognize patterns in its training data that indicate the likelihood of rainfall. Those patterns might include high temperatures, low air pressure,
- Evaluate the model. AI designers and engineers use the validation set they prepared earlier to assess their model's ability to predict rainfall accurately and reliably. Analyzing a model's performance can uncover potential issues impacting the model, such as insufficient or bias
- Deploy the model. When the AI designers and engineers are satisfied with their model's performance, they deploy it in an AI tool—helping people in their city stay dry on their way to work!
Example tools include:
Description: Anthropic Claude can complete problem-solving tasks, like finding mathematical solutions, translating between languages, and summarizing long documents.
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Description: Supercharge your creativity and productivity with Gemini. Chat to start writing, planning, learning and more with Google AI.
Stand-alone or integrated: Both
Description: Integrated with Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Copilot can help with online searches to find information, compare products, and summarize web page content.
Stand-alone or integrated: Both
Description: ChatGPT can generate ideas, plan schedules, debug code, and proofread text.
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Productivity and writing assistants
AI productivity and writing assistants can help with workplace tasks. They might provide grammar or spelling suggestions, generate a summary of a long document, or solve problems. Here are some examples:
Description: Clockwise is a calendar tool that learns users’ work habits to automatically schedule and manage calendar events.
Example industries: Consulting, technology, sales
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Description: Grammarly is a writing assistant that can help users edit and write clear, concise text.
Example industries: Creative writing, education, marketing
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Description: Jasper is a writing assistant intended for marketing tasks, like drafting social media posts, emails, and landing page content.
Example industries: Copywriting, marketing, sales
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Description: NotebookLM integrates into document apps, like Google Docs, and helps summarize or ask specific questions about text, notes, and sources.
Example industries: Content writing, finance, sales
Stand-alone or integrated: Both
Description: Notion AI is a writing assistant built into Notion, a productivity and note-taking software tool.
Example industries: Development, marketing, product management, sales
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: AI by Zapier is a built-in productivity tool that allows AI automation to be integrated with the apps and workflows already connected through Zapier.
Example industries: Engineering, marketing, project management, technology
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Code-generative AI tools
Code-generating tools can help generate, edit, or complete code for a variety of programming tasks in many different programming languages. Examples include:
Description: Built into Android Studio, Studio Bot can generate code and answer questions about Android development.
Example industries: Data science, software development, web development
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Built into GitHub, Copilot can write and suggest code, suggest descriptions for pull requests, translate multiple languages into code, and index repositories.
Example industries: Data science, software development, web development
Stand-alone or integrated: Both
Description: This tool, built into Replit, is a cloud-based Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for programmers that can make suggestions, help explain code, and turn natural language into code.
Example industries: Data science, software development, web development
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Tabnine can be a plugin to many popular code editors to help speed up delivery and keep code safe.
Example industries: Data science, software development, web development
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Description: Jupyter is an open-source platform for coding, and this built-in tool includes a chat interface, which can be used to generate code, fix coding errors, and ask questions about files.
Example industries: Data science, software development, web development
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Image and media generative AI tools
Media-generating AI tools help workers with tasks like generating and editing images, video, and speech. Examples include:
Description: Built into the Adobe suite, Firefly can generate and edit images.
Example industries: Design, education, marketing
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Canva Magic Design is a tool that generates text and image content in Canva, an online graphic design tool.
Example industries: Design, education, marketing
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Integrated with ChatGPT, DALL-E generates images from text prompts.
Example industries: Design, education, marketing
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: ElevenLabs is a speech AI tool that can generate spoken voice-over audio from text in different languages.
Example industries: Content creation, education, marketing, production
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
- Description: Google Ads helps businesses reach customers around the world, driving growth and performance. Google Ads makes it easy to create campaigns, measure impact and improve your results. Put Google AI to work for your business with theGoogle Ads AI Essentials. Learn more with theAI Explored video series.
Example industries: Marketing, Advertising
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Integrated into Discord, Midjourney can generate images from text prompts.
Example industries: Design, education, marketing
Stand-alone or integrated: Integrated
Description: Runway can generate a new video from a text prompt or edit an existing video’s style or focus area, and remove people or other elements.
Example industries: Content creation, design, marketing, production
Stand-alone or integrated: Stand-alone
Importance of Human involvement in AI
Determining if Generative AI is right for the task on hand
Example where the above questions / use of Generative AI is not feasible. Suppose you want to negotiate with the local suppliers to get the best price for ingridents you want to use in your restaurant. This task is not Generative. It requires communications and relationship building where AI is not possible.
Another example
When is Generative AI not right?
- Tasks requiring specialized knowledge - For instance, a restaurateur wants to use an AI tool to draft a lease agreement for their new storefront. While the tool can generate text, it might lack the legal expertise to handle specific clauses and regulations, potentially leading to inaccurate or incomplete portions of the lease.
- Tasks requiring knowledge of personal preferences - Consider a training manager who's using an AI tool to create a customized lesson plan for a new onboarding workshop that caters to the needs of new employees. Without an understanding of each employee's roles or learning styles, the AI tool won't be able to produce an effective lesson plan.
- Tasks requiring information beyond the last training date - Tasks that require information beyond the AI's last training date cannot be reliably addressed by generative AI tools. This is due to knowledge cutoff, the concept that an AI model is trained at a specific point in time, so it doesn’t have any knowledge of events or information after that date. For example, a business owner who's preparing their 2025 tax documents might ask a generative AI tool to summarize the newest tax deductions available in 2024. However, if the AI tool was last trained in 2023, it won't produce a useful output because it lacks the information needed to complete this task.
Prompt Engineering and LLM
- LLMs are trained on massive data comprising books, articles, websites and more. This training helps models establish patterns and relationships that exist in human language.
- They can also predict what word is likely to come next in sequence in a sentence.
LLMs can compute the probability of word that comes next - wet has the highest probability, whereas damp has lower, whereas dry has much less probability.
Key principles of effective prompts / Prompt Engineering
- Use verb to tell what exactly to do -- for example, Create an outline of an article.... Edit the language for non technical audiene, etc.
- Provide context.
Recognize Data Bias and AI Harms
- Model is as good as the data it receives.
- Systemic bias exists in social systems.
- The data in these systems may already be biased since humans are influenced by systemic biases.
- More the data represents a wider variety of people, the more inclusive the outcome of the image generation will be.
- AI are value-laden / it is not intrincically value neutral, therefore requires critical thinking when applying them.
- AI models reflect biases of the data they were trained on.
- AI models also reflect the values of the people who designed them.
AI Harms
Example: If a property manager for an apartment complex were to use an AI tool that conducted background checks to screen applications for potential tenants, the AI tool might misidentify an applicant and deem them a risk because of a low credit score. They might be denied an apartment and lose the application fee.
Example: When speech-recognition technology was first developed, the training data didn’t have many examples of speech patterns exhibited by people with disabilities, so the devices often struggled to parse this type of speech.
Example: When translation technology was first developed, certain outputs would inaccurately skew masculine or feminine. For example, when generating a translation for words like “nurse” and “beautiful,” the translation would skew feminine. When words like “doctor” and “strong” were used as inputs, the translation would skew masculine.
- Feminine / masculine speech....
-- example is deepfakesExample: If someone were able to take control over an in-home device at their previous apartment to play an unwanted prank on their former roommate, these actions could result in a loss of sense of self and agency by the person affected by the prank.
Drift
Checklist for using AI responsibly
- Identify potential harms by prompting the AI tool with different examples and checking the outputs.
Test the tool on topics you’re familiar with, so you can verify outputs with your own knowledge.
To minimize the effects of hallucinations:
Always make sure your prompt provides context, includes an example, and states a request.
Avoid using a false premise in your input. Make sure your prompt is clear, specific, and accurate.
- Tell your audience and anyone it might affect that you’ve used or are using AI. This step is particularly important when using AI in high-impact professional settings, where there are risks involved in the outcome of AI. Explain what type of tool you used, describe your intention, provide an overview of your use of AI, and offer any other information that could help your audience evaluate potential risks. Don’t copy and paste outputs generated by AI and pass them off as your own.
- Fact check content accuracy using search engines.
- Ask yourself: If this content turns out to be inaccurate or untrue, am I willing or able to correct my mistake? If you aren’t, that’s probably an indicator that you shouldn’t share it.
Only input essential information. Don’t provide any information that’s unnecessary, confidential, or private, because you may threaten the security of a person or the organization you’re working for.
Read supporting documents associated with the tools you’re using. Any documentation that describes how the model was trained to use privacy safeguards (such as terms and conditions) can be a helpful resource for you.
If I use AI for this particular task, will it hurt anyone around me?
Does it reinforce or uphold biases that may cause damage to any groups of people?






























No comments:
Post a Comment